NetCracker ordered to conduct this research called “Advanced analytics of business drivers and use cases: communications service provider approaches to leveraging data from Network”, detailed presentation you can find below. Here is a shortened description.

Business drivers and approaches.
These days, customers can satisfy their needs in digital products or services instantly. Therefore for clients a possibility of switching to other communications service providers’ (CSPs) increased.
Actually, global research was published by Ovum in Telecoms Customer Insights 2014 that includes data about 25% of all users who say they will change CSP with another quarter indicating they may do so, within the next year.
While the trend of churn varies cardinally independence of a country and CSP, the threat is existing. Also, GSMA Intelligence data shows that monthly average revenue per user has dropped about 4 percent in the last year. In addition, there is good news for new players. It’s a direct link between a broadband service quality and share price that was found by Europe’s investors.
A lot of CSPs are aware of the tendency of churn and are designing a strategy aimed at decreasing or stabilizing users migration. Actions are directed to raise the agility and use of high technologies, but mostly CSP’s are focusing on the customer experience.
As the main source of data, CSPs are often using network and service data especially at a step of planning and designing. CSPs are researching data and applying sophisticated analytics of retrospective and real-time data to learn how to give the best service, quality products, and price to predict and decrease the churn.
CSP networks possess information about subscribers, applications and network state. To increase the value delivered to subscribers and differentiate their fixed and mobile broadband services, they have to optimize the value of their network resources and use a huge quantity of data they possess.
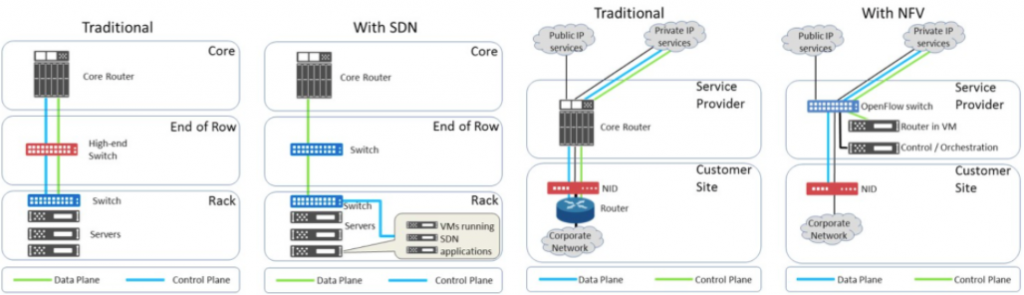
The potential benefit connected with network intelligence is significant. New network technologies such as NFV and SDN, provide new possibilities for network and software optimisation. NFV is the concept of a network architecture in which the virtualised whole classes and feature sets of network nodes. They may be linked, joined to form a telecommunications service. That is, these functions are presented in the case of virtualisation at the software level, abstracted from the physical, and can be delivered from the cloud.
This approach allows the operator to launch new services without the purchase of new equipment and to solve the problem of its compatibility with existing ones.
Using NFV allows you to build a flexible, stable working and economical network architecture that can quickly and easily adjust following the increase or decrease of the volume of the traffic.
To virtualise networking features bring the most benefit, it is necessary to use a software-configurable network (SDN). SDN technology allows operators to manage network resources, presenting them as virtual services. Network services also need to virtualise to achieve the same flexibility and simplicity in the NFV. Without this, it is impossible to fully realise the potential of NFV. In addition, the use of SDN expands NFV due to better traffic organisation.
SDN and NFV
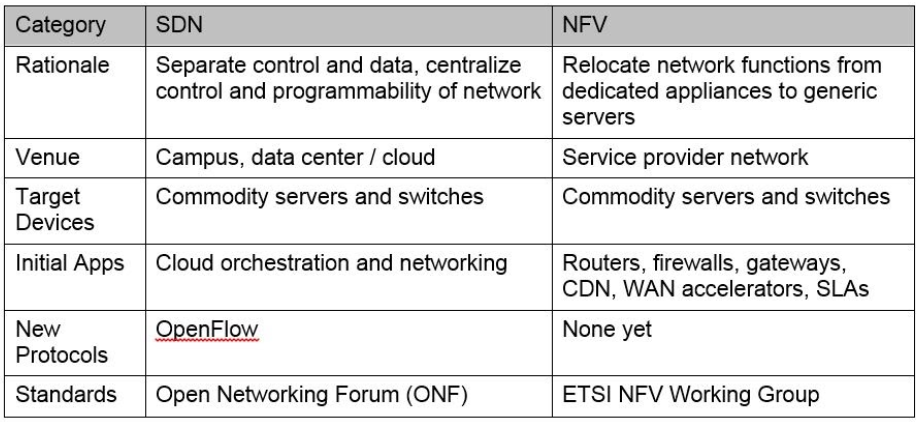
Using techniques SDN and NFV divides the network into virtual layers or segments, and thus simplifies the management of each of them and the whole network. In addition, each segment is responsible for the provision of certain services, and it is configured for optimal performance.
As a result, one the physical network ensures reliable operation of a variety of services with its own settings. In this case, the operator has the opportunity to exercise individual control of each layer or set the same management options for multiple layers simultaneously. In particular, due to network segmentation is possible to create a virtual mobile operators (MVNO).
The network segmentation simplifies network management, working with static settings. It also gives an opportunity to change the functional of segments and perform an upgrade.